Neuroscientist Michael Graziano has speculated on the connection between the material and the spirit world. His book “God Soul Mind Brain” has the stated aim to describe ‘the mechanistic understanding of the spirit world’. With is background he makes the assumption that ‘mechanism’ is the reality and perception is the illusion.
“we do not perceive the world as it is, the brain constructs a simulated world”
“colour is not actually out there…. The same set of wavelengths may look green to you in a different context or grey or blue”
“We experience the model rather than the reality”
The statements are fascinating reminders of what the brain does: it constructs a simulated world, it provides the stimulus to allow the experience of colours, it somehow appears to create a model in our brains.
However, it is a false assumption that the mechanism is the reality and the perception is the illusion. Accepting the assumption is like saying that the material pages of a book and the printed ink are the reality, and the story that the book tells or the information that it contains is not the reality. Whist nobody would disagree that the book is the material and the story is not, which of them is the reality?
In a book, we read the words rather than perceiving the paper and letters and we construct in our imagination a picture and an experience based on the words and story within the book. In the only scale of importance that matters to a human being, the book is the words, not the paper and ink. War and Peace is a famous story, the paper that it was written on was just the framework for holding it. The story is eternal although the paper decays. To a human being, the story is the reality.
Consider a work of art; the material is not the masterpiece, it is merely a framework which holds the masterpiece. The canvas and paint is meaningless, the picture is the meaning.
If we can free ourselves of the dogma of materialism then we can perhaps begin to consider that in the universe created from nothing, where particles are only potentialities until they are observed the reality is the experience, the qualia, the ‘I’, and that the material is just the skeleton for holding the reality.
The material universe is meaningless until it is perceived, the perception of it gives it meaning.
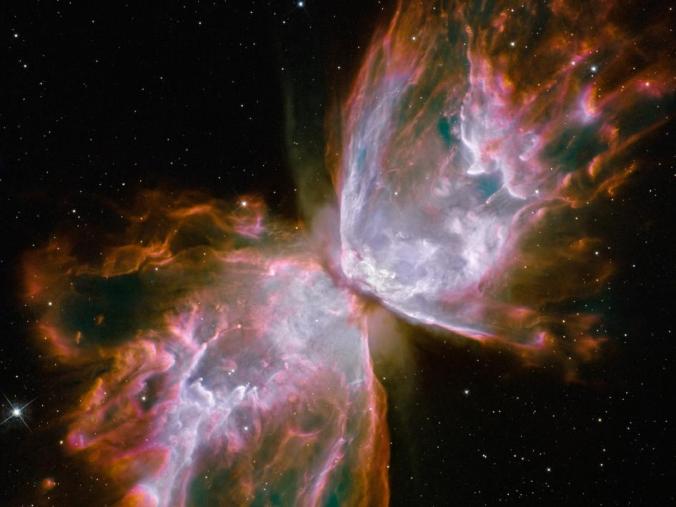
The butterfly nebula is beautiful when it is observed; without observation it is meaningless.
Two bags of chemicals are meaningless, but the intimate relationship between two people who are in love has immense meaning and purpose.
Is this so strange? When we look at the quantum level of the material, there is no such thing as paper or ink. There are particles and forces that we cannot understand. They are outside of our ability to perceive, so we think of them as miniature versions of ping pong balls and sticks. They are only potentialities until they are observed. What we consider material reality is not really real, it performs its function only when it is perceived and observed. So perhaps what we perceive as real day to day, the material world, is similarly non-material. Perhaps the only reality is our perception, our model.
So what of God in this? Jesus spoke of God living in us and us in him. Perhaps our material framework that holds us is part of God. As Anselm wrote, everything is what it is through extreme goodness, through God, so we are what we are through and within God. We are told that God is love, and that we are made in his image. Jesus said that ‘if you have seen me, you have seen the father’; I don’t think he was talking about his flesh, but his ‘being’ – his ‘spirit’. Our framework (our body and brain) is a small part of a material universe that is created and sustained by God. If that universe is within God, part of God, then we too are ‘in him’, as he is ‘in us’.
And what of laws of physics, of evolution and biology? We can create mathematical models of inanimate physical objects, and we can observe the behaviour of molecules and cells which seems to be beyond the possibility of simply responding to those physical laws – yet seems to be consistent, predictable, and purposeful. Within the framework where the universe is within and part of God there may be causes other than the laws of physics for the astonishing growth and development of the human being from the single cell; a God whose will ‘knits us together in our mother’s womb’. In the same way that our ‘will’ causes our hands to move, makes our choices, interacts with others, so God’s will can cause our bodies to grow and develop, to form our brain, to manufacture us as the masterpiece we are, our body being the receptacle for our spirit.
It is the non-material that motivates us, the non-material that leads to change, the non-material that makes our world like it is rather than a desolate moonscape. The non-material is master over matter. The non-material is the meaning, the meaning is the reality.
Who would disagree that there is a ‘spirit of Christmas’, all of society embracing a season of joy and giving. People speak of the true spirit of Christmas; we know that there is something that transcends each of us as individuals. It is part of the sprit that is God.
When we observe a beautiful woodland track, sunlight shining through the leaves to create a dappled light settling on a trickling stream, that beauty is part of the essence that is God.
When we listen to a sublime piece of music that moves us to tears, or an energising rock ballad that lifts our hearts with passion, that is part of God.
When we love someone, our love is part of the supreme love that is God.
When we meet friends in a party, in a community, that spirit of community is part of God’s spirit of community.
If we can appreciate that the greater reality is the spirit, and the material is just the framework then we can see God and the universe in a whole new light. The universe can be considered the canvas for a cosmic work of art, a magnificent symphony of action and awe. Life is a molecular dance of astonishing intricacy and beauty. We are permitted to explore and understand through science. We are permitted to glimpse the canvas and participate in the dance; characters created by the dance emerging as individual caring, loving, interacting beings partaking of some of the glory that is the story; individual masterpieces beyond the beautiful, whose reality is our character, our choices, our nature, our soul. Creatures of purpose and with purpose. Creatures honoured with the possibility of relating to our creator, the master artist, engineer, scientist, musician, teacher, parent, friend, but never are we his equal.
So this is the God of Science: A God who was there before the universe began. An un-created, creator God who gave ‘nothing’ the ability to become ‘something’. A God who sustains, and maybe actually is, the very fabric of the universe. A God who actually is the laws of physics, who benevolently guides providence to bring life out of a set of chemicals. A God who imbues the chemical dance that is us with the ability to feel, to taste, to see, to experience: love, joy, peace, fulfilment, intellectual challenge, selflessness, forgiveness, anger, hate, disgust, bitterness. Perhaps even a God who is love, joy, peace, fulfilment…. But a God who allows us to experience both the good and the bad, and who allows us to choose to pursue that which is good, or that which is not.
Add to this the God revealed to us by Jesus Christ and we begin to understand the complete context.